How does waste from electronics industry impact the environment?
To meet the increasing demand of using electronic equipment, domestic and foreign enterprises have been actively investing in building a lot of factories and production workshops to supply electronic components for foreign businesses in the electronics industry having factories in Vietnam. This brings many benefits to the development of the domestic electronics industry, as well as creating conditions to attract foreign enterprises to invest here.
However, in parallel with that, the amount of waste from the electronics industry is increasing and badly affecting the environment if not handled in a timely and reasonable manner. So what is the current situation of the waste from electronics industry? What is its impact on the environment and the solution to this problem? What have businesses been doing to address these issues in environmental protection? The article below will analyze the current situation, the impact of electronic waste on the environment as well as the solutions to e-waste.
1. Current situation of waste from the electronics industry in the world
According to the European Environmental Agency (EEA), the amount of electronic waste disposed in the world each year has reached 40 million tons, which is currently growing three times faster compared to other types of waste. The main reason for this is the continuous increase in consumption of electronic goods. According to the 2014 report from Emarketer, only in terms of cellular phones, there were 1.64 billion users worldwide, this number was estimated to increase to 2.56 billion, equivalent to one-third of the global population in 2018. That shows the number of people who have been using electronic devices is increasing indefinitely.
In addition, the technology is constantly updated and improved, resulting in a shorter life span for electronic products, which in turn necessitates the continuous production of electronic components for new equipment. This is also considered one of the causes of electronic waste to rise dramatically. This has a great impact on the economy and human life, especially the environmental problems in the countries being invested.
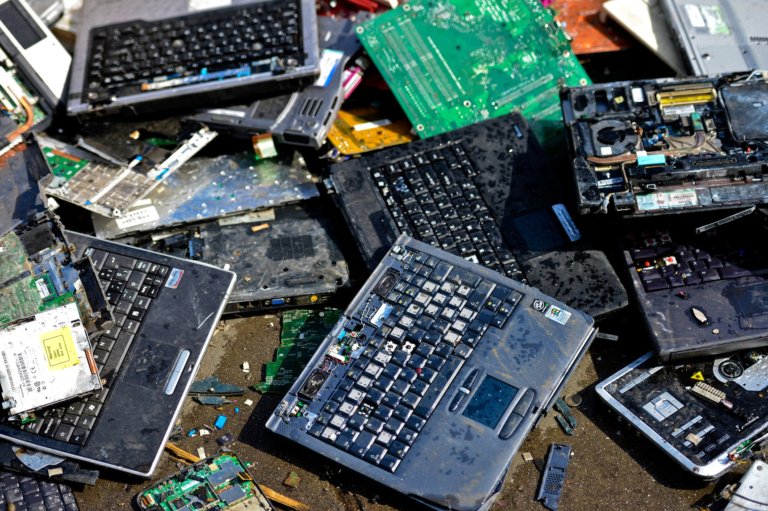

2. The impact of waste from the manufacturing of electronic component, equipment industry on the environment
Waste from the manufacturing of electronic component, equipment industry mainly comes from two main sources, which are waste in the process of producing and waste from daily activities of workers at the factory.
The composition of waste from electronic components industry contains many impurities, metals as well as toxic chemicals. Moreover, the daily waste resulting from the dietary needs, sanitation of workers also contains many organic compounds and harmful bacteria. Both types of waste are the main causes of bad effects on the environment without proper and reasonable treatment process.
According to research by Silicon Valley Toxics Coalition, based in San Jose, California, electronic waste can spread and leach various types of harmful substances in mercury, barium, Beryl, zinc or lead into water and air. This is extremely dangerous for the health of the people living around the electronics manufacturing sector. For example, lead can harm the nervous system, blood circulation and kidney of young children; Bari causes heart damage and swelling of the brain; Beryl causes lung cancer, etc. Therefore, electronic waste treatment is an urgent and necessary task that the government as well as the production enterprises need to pay attention.
Request for Consultation
Flexible spaces ranging from 250 - 10,000 m²
3. Treatment solutions for waste from the electronics industry
a / For the Government
With the serious effects of the waste, the government has enacted general regulations for the treatment of electronic waste for businesses investing in the electronics industry to protect the environment of people in the most effective way.
According to the Circular of the Ministry of Industry and Trade on the provisional regulations in the limit of permitted levels of toxic chemicals in electrical and electronic products No. 30/2011/TT-BCT, electronic equipment in Vietnam market must ensure the level of toxic chemicals to not exceed the permission level of the government. Additionally, some chemicals cannot be used or are restricted in electronic products including Mercury (Hg), Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Chlorine 6 (Cr6 +), Polybrominated Chromate Diphenyl ether (PBDE) and polybrominated biphenyl (PBB). This regulation aims to reduce the amount of toxins present in electronic devices to limit the impact of these products on users.

Besides, the HCMC Department of Natural Resources and Environment in cooperation with many other donors have made Vietnam recycling program with the aim of collecting electronics waste to overcome the processing and distribution Destruction of indiscriminate waste that pollutes the environment to overcome the situation of indiscriminate waste disposal and decomposition that pollutes the environment.
b/ For enterprises
Not only the govenrment, enterprises in the field of electronics industry also need to have appropriate waste treatment measures to protect the environment. That means that manufacturers must develop a strict and efficient industrial waste treatment process. At the same time, these units also need to have standardized treatment systems in accordance with current state regulations on industrial waste disposal, including steps such as: separate large scale sludge such as sand, crushed stone, metal, etc.; must have a tank to stabilize the flow and concentration of waste; must have color and odor treatment system of waste;

With the above analysis, we can see how serious the impact of electronic waste on people’s living environment. The current solutions of the government and investors in Vietnam are not really the most effective. Hopefully in the near future, our government and businesses will cooperate to build and implement more strictly in the implementation and handling of electronic waste.
By Marketing Department – Kizuna JV Corporation
Sources: https://www.emarketer.com